What is IoT? A Beginner’s Guide to the Internet of Things

- Tech Insights
- December 10, 2024
- Techizzle
We’re living in an era where almost everything around us is connected. From your thermostat to your refrigerator, your devices are all talking to each other and to you. This interconnected universe is powered by the Internet of Things (IoT), a groundbreaking technology blurring the lines between the physical and digital realms. As we step into the future, IoT continues to revolutionize how we live, work, and interact with technology, promising a smarter and more efficient future.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is IoT?
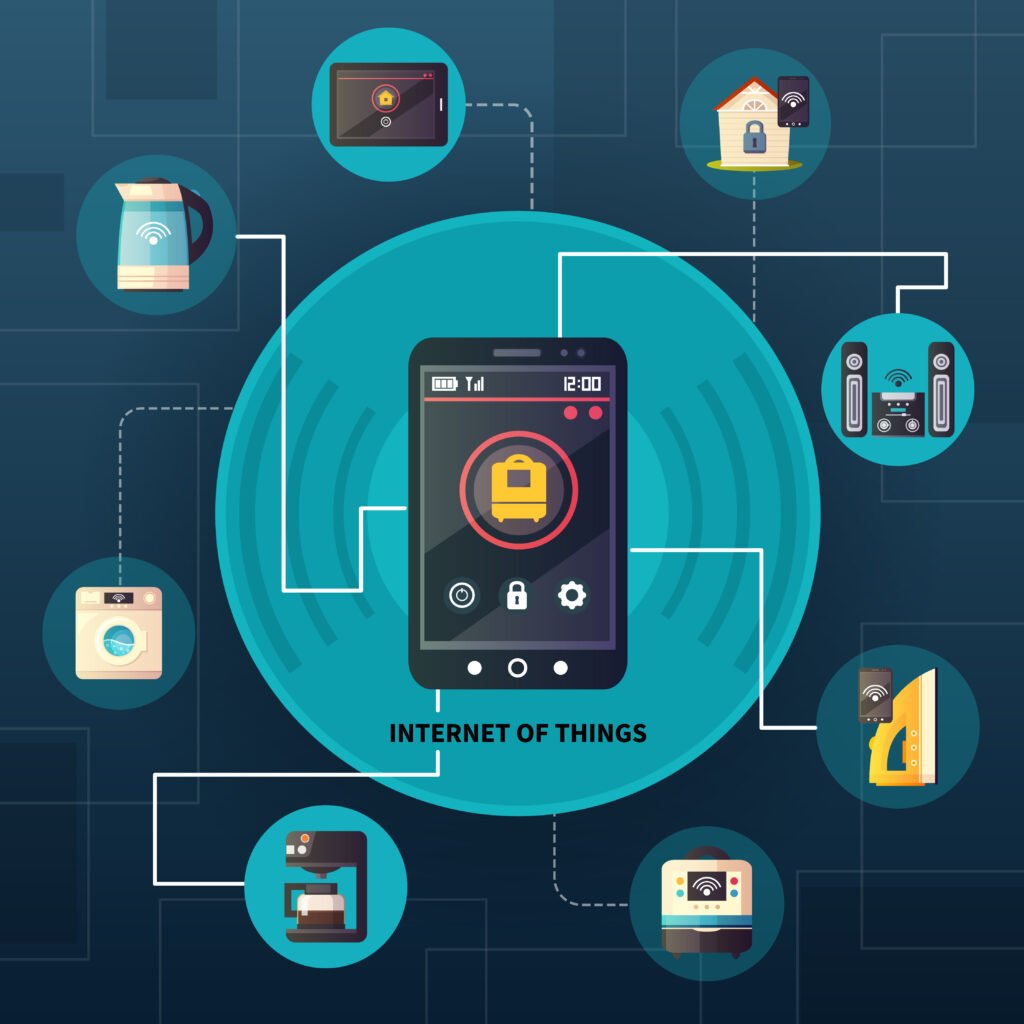
If I talk about its core, the Internet of Things (IoT) is all about connectivity. It is the idea of everyday objects. Whether they’re your car, your clothes, or even your coffee machine can be connected to the internet and to each other, creating a network of devices that work together. These devices are equipped with a tons of various sensors, software, and other tech that allows them to collect data and communicate for better user experiences.
For example, think of your smart watch: it tracks your steps, monitors your heart rate, and sends health alerts to your phone. Or your connected home system that adjusts your thermostat, locks your doors, and dims the lights all with a simple voice command. These are just some of the everyday ways IoT is making life more convenient, efficient, and, well, just a little bit cooler.
How IoT Works?
So how does this all come together? IoT works through a combination of three main components: devices, connectivity, and data.
Devices and Sensors: At the heart of IoT are the sensors that gather data. These can be anything from simple temperature sensors to advanced motion detectors or cameras. Think of them as the eyes and ears of the IoT network.
The Role of Connectivity: Of course, the sensors can’t do much without a way to communicate. That’s where connectivity comes in. IoT devices typically use Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, or cellular networks to send the data they collect to a central hub or the cloud.
Data Flow: Once the data is transmitted, it’s processed and analyzed to create actionable insights. For example, your smart thermostat doesn’t just collect data about the temperature—it learns your preferences and automatically adjusts to keep you comfortable while saving energy.
Applications of IoT

IoT is everywhere, and its impact is felt across many different industries, including smart homes where devices enhance convenience and security, healthcare with remote patient monitoring and smart medical devices improving patient care, industrial sectors utilizing predictive maintenance to optimize operations, agriculture through precision farming techniques that increase yields, and smart cities leveraging connected technologies to improve urban living and resource management. Let’s see some examples:
1. Smart Homes
- Smart Thermostats: Devices like the Nest Learning Thermostat learn your schedule and preferences, adjusting the temperature automatically to save energy while keeping your home comfortable.
- Smart Security Cameras: Ring doorbells allow homeowners to monitor their front door via a smartphone app, providing real-time alerts and video feeds.
2. Wearable Technology
- Fitness Trackers: Devices like the Fitbit monitor heart rate, steps, and sleep patterns, helping users track their physical activity and health metrics.
- Smartwatches: The Apple Watch not only keeps time but also tracks fitness, monitors heart health, and allows users to receive notifications and calls.
3. Industrial IoT (IIoT)
- Predictive Maintenance: Companies like GE use IoT sensors on machinery to monitor performance and detect anomalies, enabling maintenance to be performed before a failure occurs, reducing downtime and costs.
- Supply Chain Management: IBM leverages IoT to optimize supply chains by tracking inventory and shipments in real-time, ensuring efficient operations.
4. Smart Cities
- Smart Traffic Lights: Systems like those developed by Siemens use IoT to optimize traffic flow by adjusting signal timings based on real-time traffic conditions.
- Waste Management: Bigbelly waste bins are equipped with sensors that monitor fill levels and notify waste collection services, optimizing collection routes and reducing operational costs.
5. Healthcare
- Remote Patient Monitoring: Devices like the Kinsa Smart Thermometer connect to smartphones via Bluetooth, allowing parents to track their child’s temperature and share data with healthcare providers.
- Smart Pill Bottles: The AdhereTech smart pill bottle reminds patients to take their medication and alerts caregivers if doses are missed.
6. Agriculture
- Precision Farming: IoT sensors in soil can monitor moisture levels and optimize irrigation, helping farmers conserve water and enhance crop yields. Companies like CropX provide these solutions.
- Livestock Monitoring: Wearable devices on cattle can track health and location, allowing farmers to manage their herds more efficiently.
7. Transportation
- Connected Vehicles: Companies like Tesla use IoT to provide features such as real-time traffic updates, over-the-air software updates, and autonomous driving capabilities.
- Fleet Management: IoT solutions from providers like Geotab allow businesses to monitor vehicle locations, fuel consumption, and driver behavior, improving efficiency and reducing costs.
Benefits
- IoT significantly enhances efficiency and productivity by automating a wide range of processes, enabling businesses and individuals to save time and resources while providing real-time data insights that facilitate informed decision-making and optimize operations across various sectors.
Challenges
- One of the major challenges facing IoT implementation is ensuring interoperability among a diverse array of devices and platforms, as this lack of standardization can create barriers to seamless communication and integration, ultimately hindering the full potential of IoT solutions.
Risks
- The extensive connectivity of IoT devices introduces substantial cybersecurity risks, as these devices are often vulnerable to hacking and other malicious attacks, which can lead to unauthorized access to sensitive information and potentially compromise user privacy and security
The Future of IoT

The future of IoT is driven by advancements in AI, 5G, edge computing, and blockchain. These technologies will enable smarter devices, faster connectivity, and enhanced security, transforming industries like healthcare, manufacturing, and smart cities for greater efficiency, real-time data processing, and improved user experiences. Furthermore, blockchain technology will play a vital role in securing IoT networks, ensuring data integrity, and enabling decentralized control. Together, these technologies will transform sectors such as healthcare, transportation, smart cities, and manufacturing, creating more interconnected, streamlined, and resilient systems that benefit both businesses and consumers alike.
Conclusion: Embracing the IoT Revolution
IoT isn’t just a passing trend—it’s a technology that’s changing how we live, work, and play. Whether it’s improving healthcare, creating smarter cities, or simply making our homes more comfortable, IoT is shaping the future in extraordinary ways.
The IoT revolution is already here—and as it continues to evolve, it’s more important than ever to understand its potential, its challenges, and how it will shape the world around us. Are you ready to embrace the connected future?